Python
To run the analysis and reproduce the code in Python, you will need to set up the Python environment to:
- Execute the Jupyter Notebooks of the Lab sessions of the course.
- Prepare your own Jupyter Notebooks for the assignments.
Do not try to run Python code in RStudio. Only run in Jupyter Notebooks (.ipynb) with the Python environment provided.
We will use Miniconda to handle our working environment.
Set up Miniconda (and Python) on Ms Windows
Installation
Install Miniconda:
Option 1: On a UoL Machine: Anaconda is installed on many university machines. Please check whether it is installed. If not, download and install Anaconda through from
Install University Applications, type and chooseAnaconda.Option 2: Recommended - Install Miniconda on your personal Laptop: Follow the instructions here.
During the installation, leave the default settings. In particular, when asked whom to “Install Miniconda for”, choose “Just for me”.
If you do choose to work on University Machines
- Chose a machine where Anaconda has been pre-installed.
- Always use the same machine. For example if on the first day you are using CT60 Station 17 - Orange Zone, continue using this machine for the rest of the course. If you change machine you will need to re-install the environment every time.
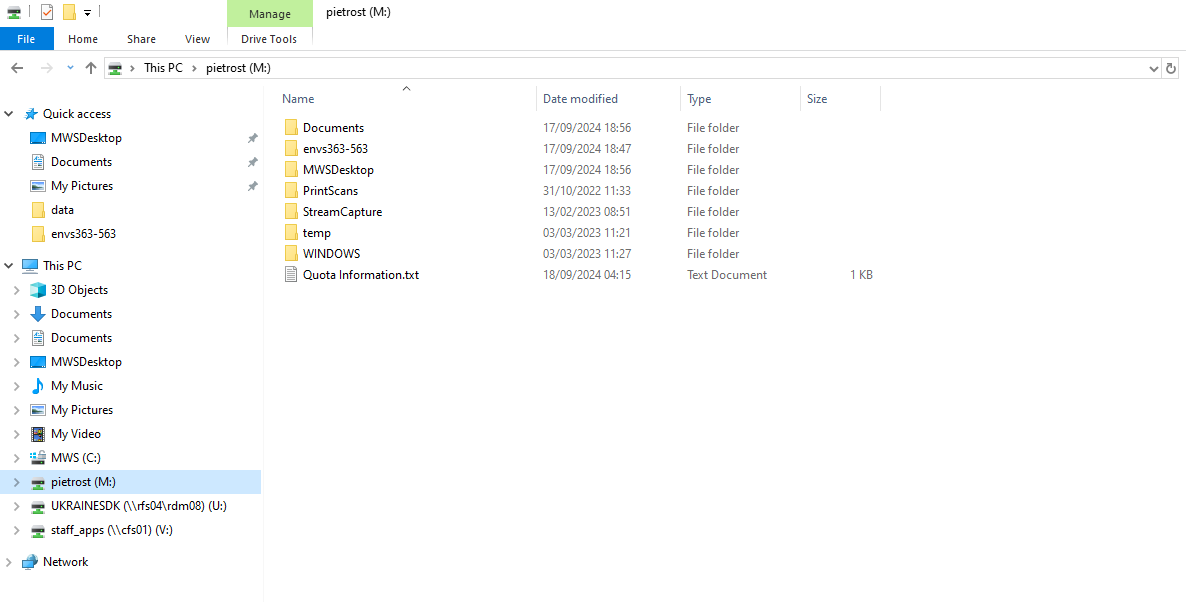
Set up the Directories
- Create a folder where you want to keep your work conducted throughout this course. For example, call it
envs363_563. You can save it wherever you want. If you are working on a university machine, it could be worth creating it inM:/, which is your “virtual” hard-disk.
- Download the data to run and render the jupyter notebooks. To learn how to download folders from github see here.
- Unzip the folders and move the nested folders into the folder
envs363_563. - Create another folder called
labs
The folder structure should look like:
envs363_563/
├── data/
└── labs/Set up the Python Environment
- Download the
envs363_563.ymlfrom GitHub by clicikingDownload raw file, top right at this page - Save it in the folder
envs363_563created before. - Type in the search bar and find the
Anaconda Powershell Promptif working on University Machine orAnaconda Prompt (miniconda 3)if on your personal. Launch it. The terminal should appear.
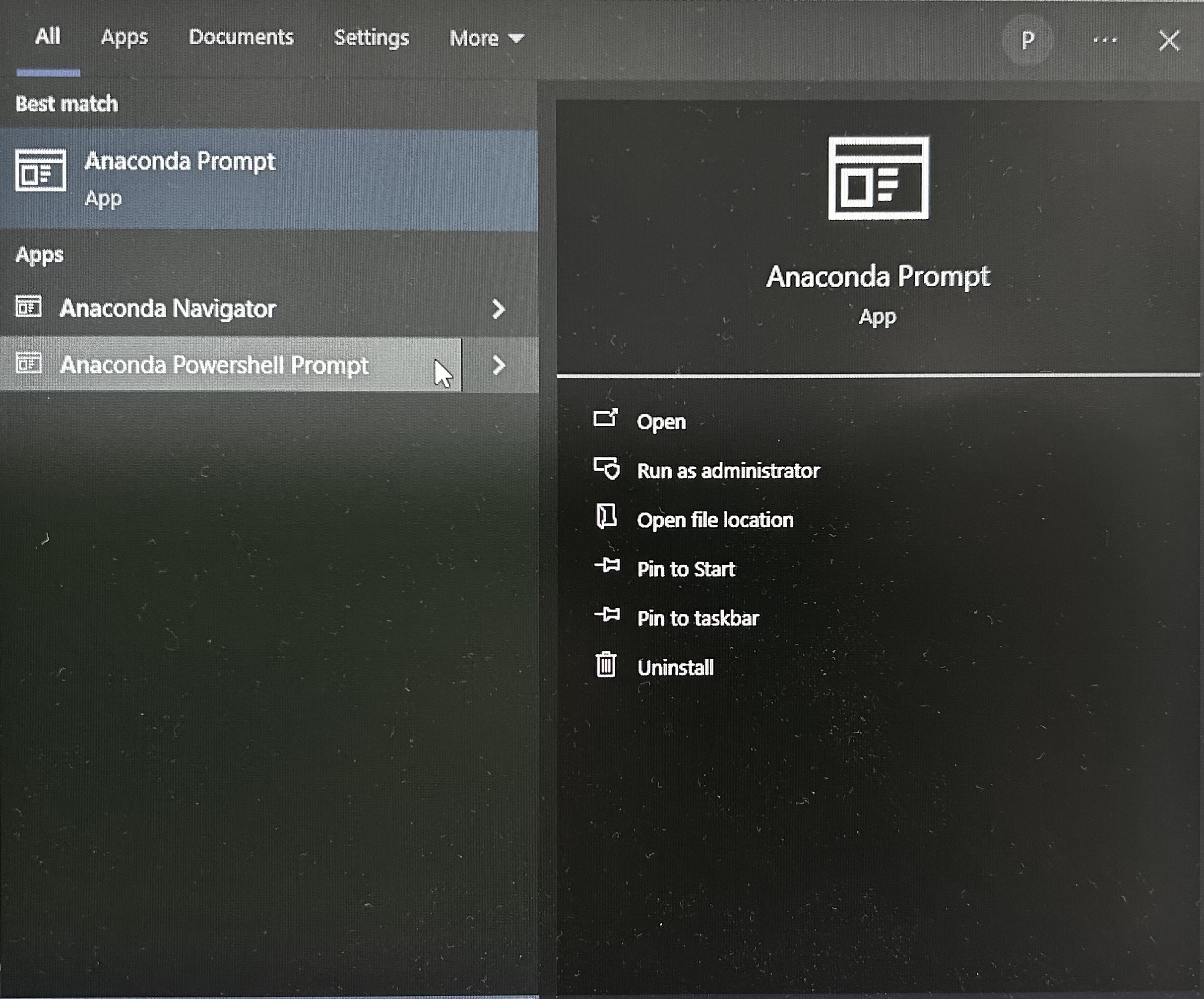
- In the Anaconda Terminal write:
conda env create -n envs363_563 --file M:\envs363\envs363_563.ymland pressEnter; if the file is located elsewhere you’ll need to use the corresponding file path. - If you are prompted any questions, press
y. This process will install all the packages necessary to carry out the lab sessions. - In the Anaconda Terminal write
conda activate envs363_563and pressEnter. This activates your working environment.

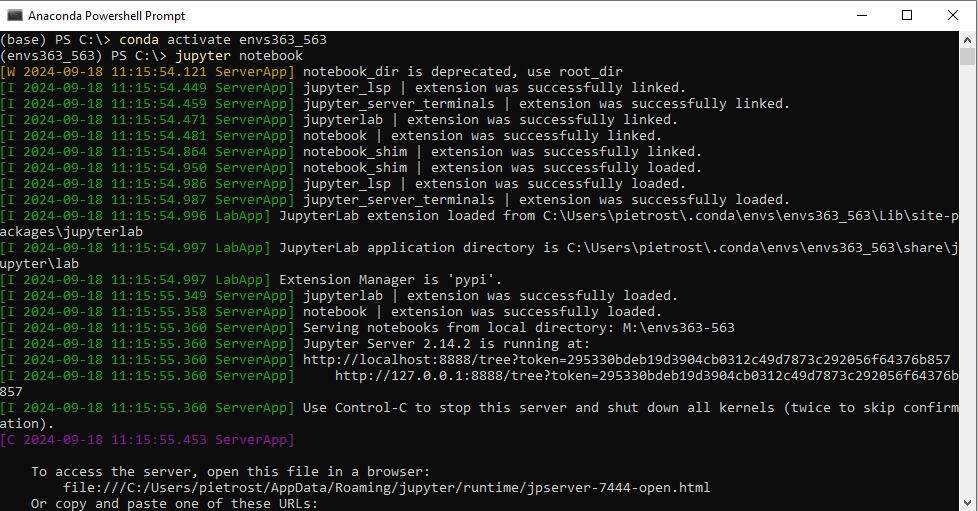
- Necessary on University machines, otherwise Optional: Configuration of Jupyter Notebooks
- In the Anaconda Terminal, write
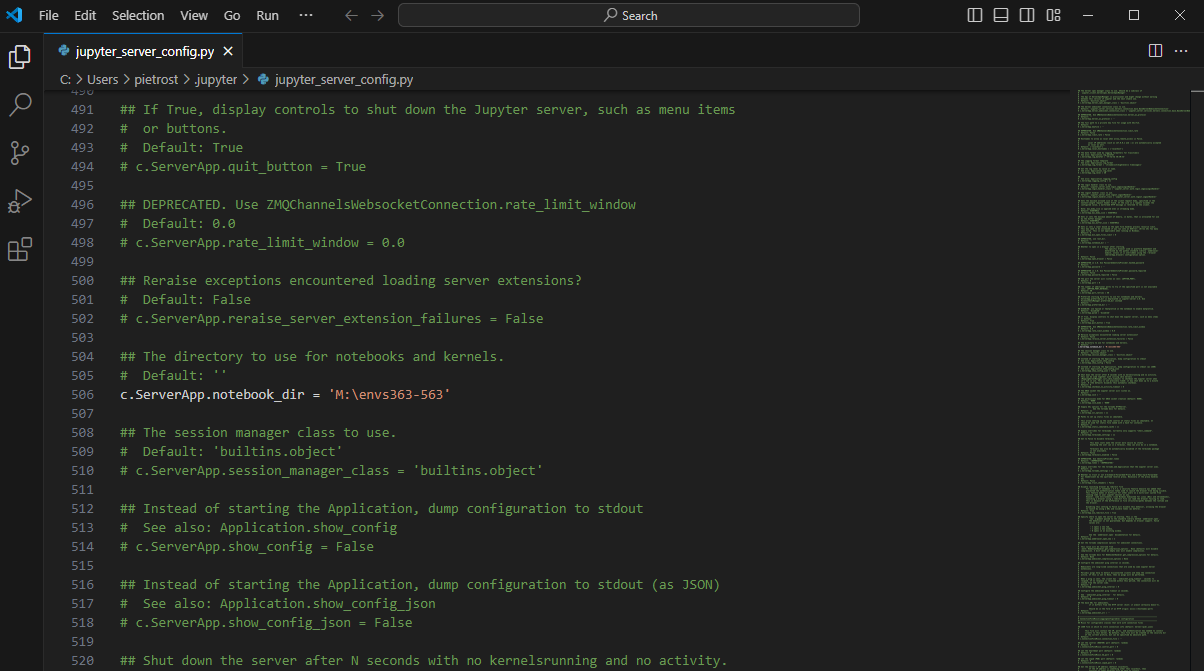
jupyter server --generate-configand press enter. This, at least in Windows, should create a file to:C:\Users\username\.jupyter\jupyter_server_config.py. - Open the file with a text editor (e.g. Notepad++), do a
ctrl-fsearch for:c.ServerApp.root_dir, uncomment it by removing the # and change it toc.ServerApp.notebook_dir = 'M:\\your\\new\\path, for example the directory where you created theenvs363_563folder. In the University Machines, it is advised to work on the directoryM:\. - Save the file and close it.
- In the Anaconda Terminal, write
Start a Lab Session
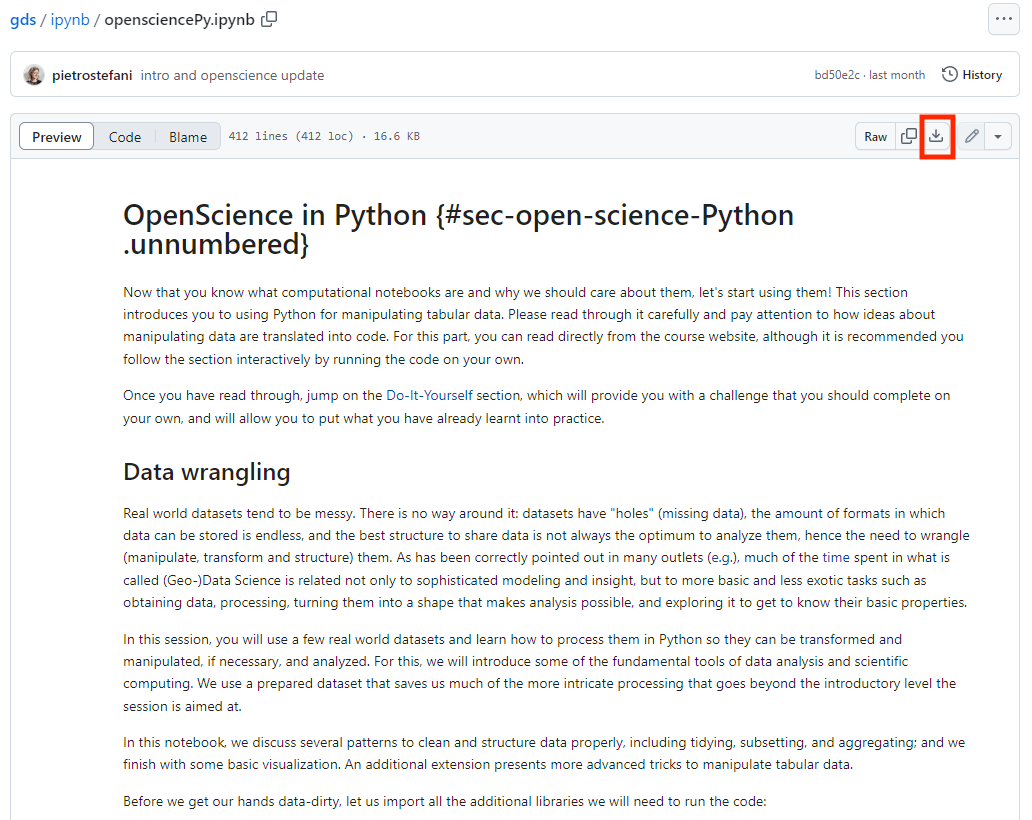
- Download the Jupyter Notebook of the session in your folder. Choose one jupyter notebook and click
Dowload raw fileas shown below.
- Save the file in the
labsfolder within yourenvs363_563folder on your machine. - Type in the search bar, find and open the
Anaconda Prompt (miniconda 3). - In the Anaconda Terminal write and run
conda activate envs363_563. - In the Anaconda Terminal write and run
jupyter notebook. This should open Jupyter Notebook in your default browser.
- Navigate to your course folder in and double click on the notebook downloaded in step 1.
- You can now work on your copy of the notebook.
Follow these instructions and test your installation prior to the first Lab Session. If you experience any issues, write a message on the Ms Teams channel of the module. Setting up the Python environment is necessary for:
- Executing the Jupyter Notebooks of the Lab sessions of the course.
- Preparing your own Jupyter Notebooks for the assignments (one each).
Set up Miniconda (and Python) on MAC
Installation
To install Miniconda on your personal laptop, Follow the instructions here. During the installation, leave the default settings. In particular, when asked whom to “Install Miniconda for”, choose “Just for me”.
Set up the Directories
- Create a folder where you want to keep your work conducted throughout this course. For example, call it
envs363_563. You can save it wherever you want. For example, Elisabetta has named her folderenvs363_563and it’s in her Dropbox inUsers/PIETROST/Library/CloudStorage/Dropbox/envs363_563 - Download the data to run and render the jupyter notebooks. To learn how to download folders from github see here.
- Unzip the folders and move the nested folders into the folder
envs363_563. - Create another folder called
labs
The folder structure should look like:
envs363_563/ ├── data/ └── labs/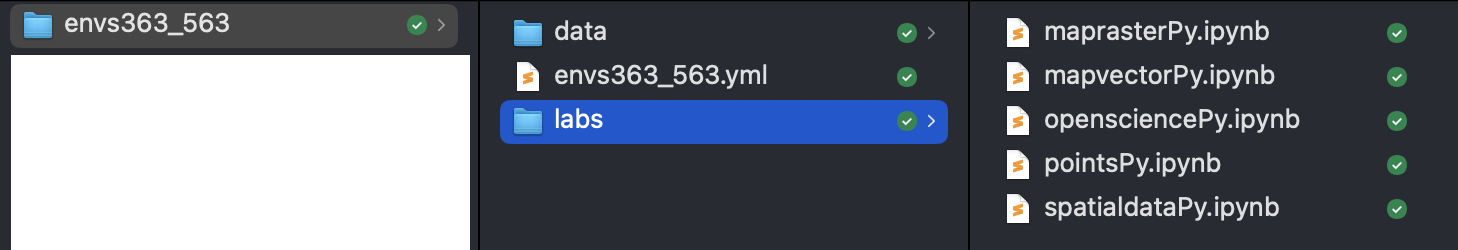
Set up the Python Environment
- Download the
envs363_563.ymlfrom GitHub by clickingDownload raw file, top right at this page - Save it in the folder
envs363_563created before. - Type in the search bar and open the Terminal.
- In the Terminal write
conda env create -n envs363 --file envs363_563.ymland pressEnter. This will need to be modified according to where you placed theenvs363_563folder. For example, Elisabetta has named her folderenvs363_563and it’s in her Dropbox inUsers/PIETROST/Library/CloudStorage/Dropbox/envs363_563/envs363_563.yml. If you created theenvs363_563folder on your desktop, the path would beDesktop/envs363_563.
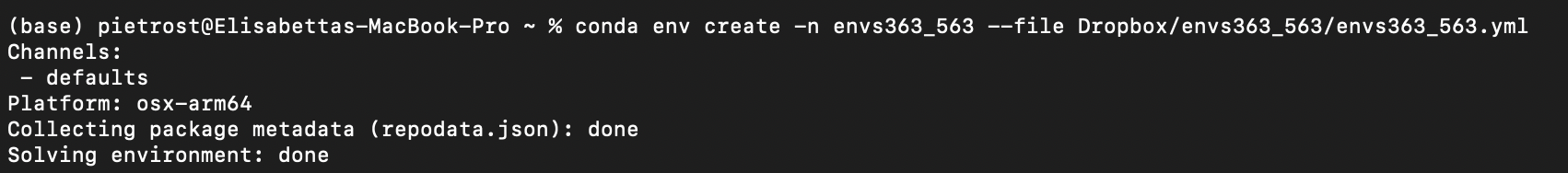
- If you are prompted any questions, press
y. This process will install all the packages necessary to carry out the lab sessions. - You should then see this

Start a Lab Session
- Download the Jupyter Notebook of the session in your folder. Choose one jupyter notebook and click
Dowload raw fileas shown below
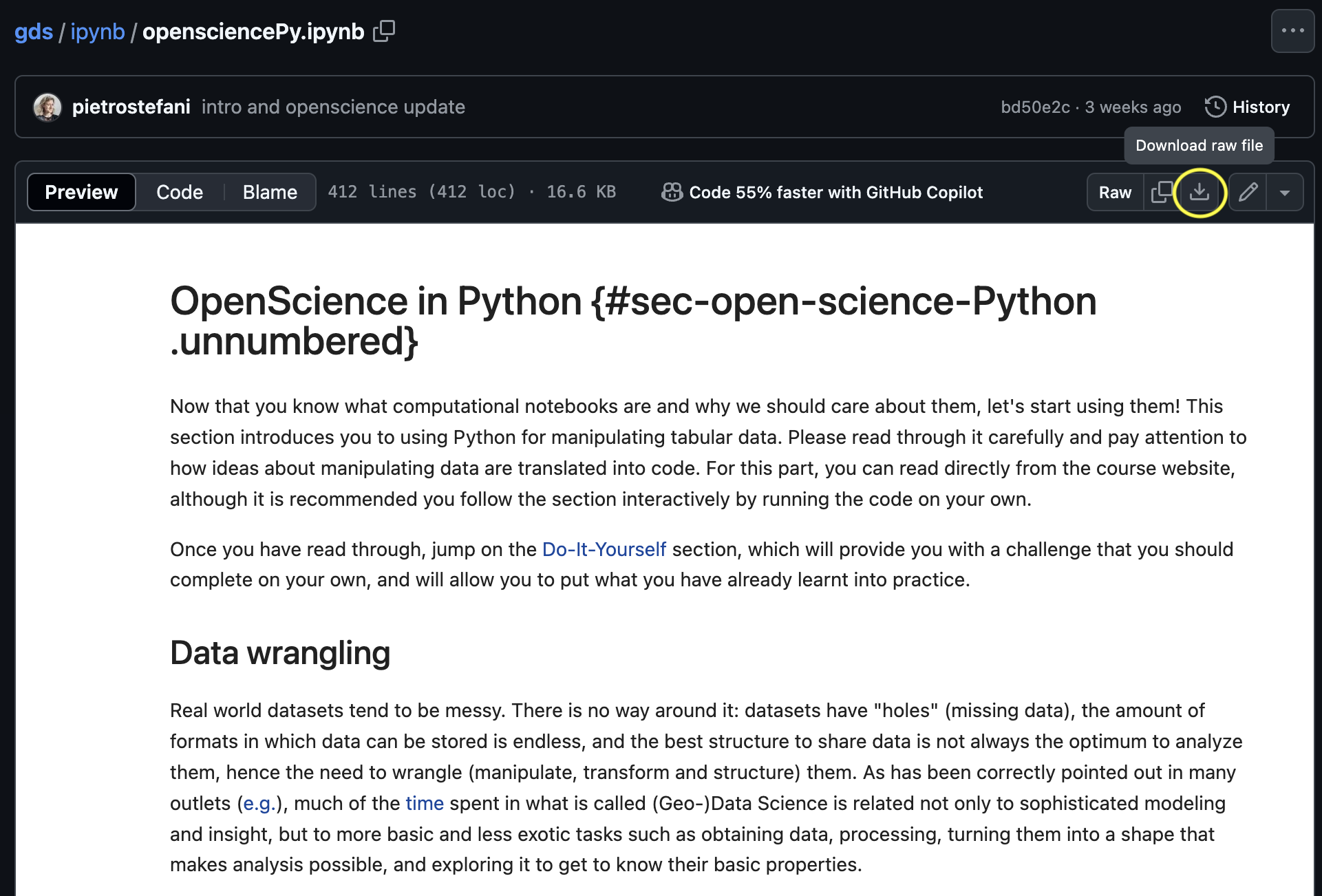
- Save the file in the
labsfolder within yourenvs363folder on your machine. - Type in the search bar, find and open the Terminal.
- In the Terminal write and run
conda activate envs363. - In the Terminal write and run
jupyter notebook.
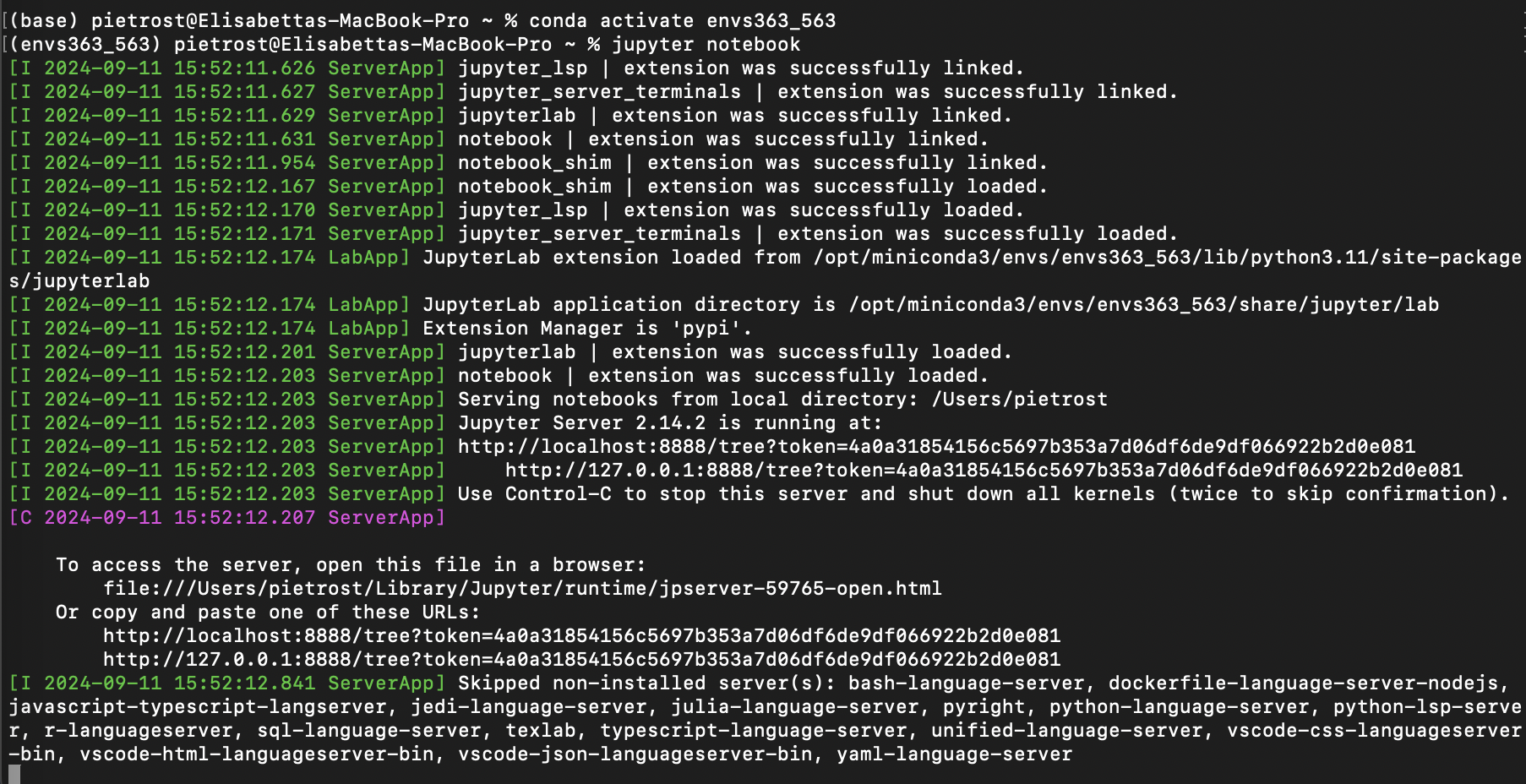
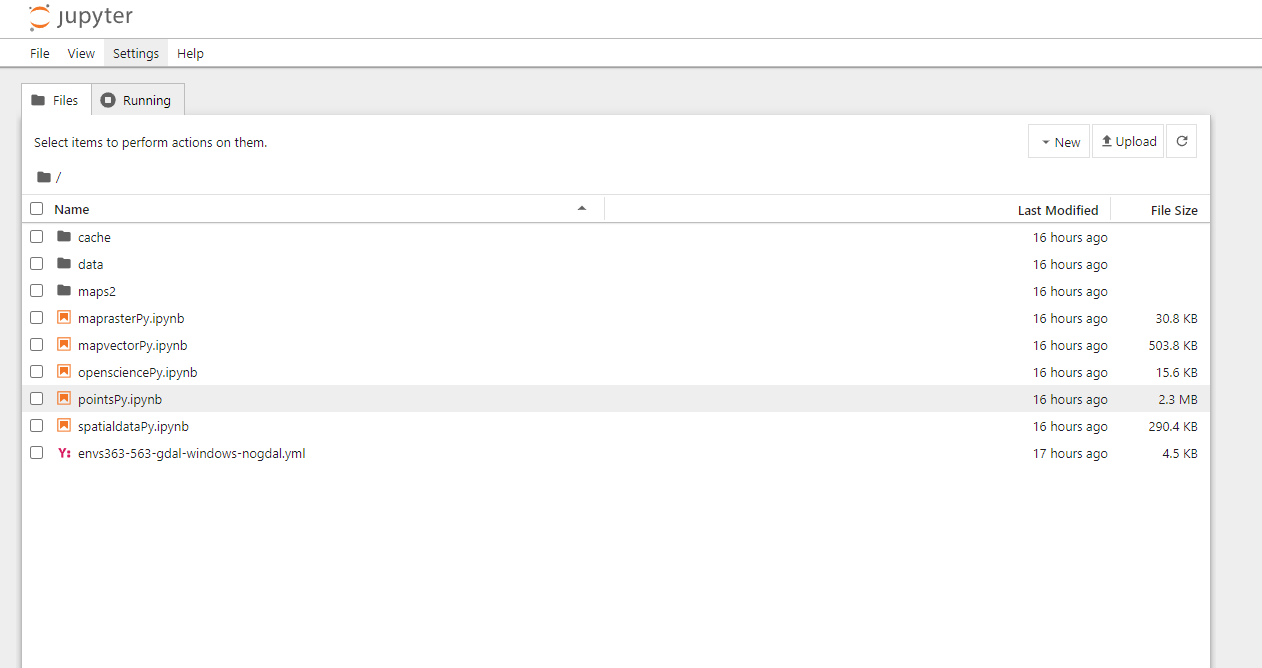
- This should open Jupyter Notebook in your default browser. You should see something like this:
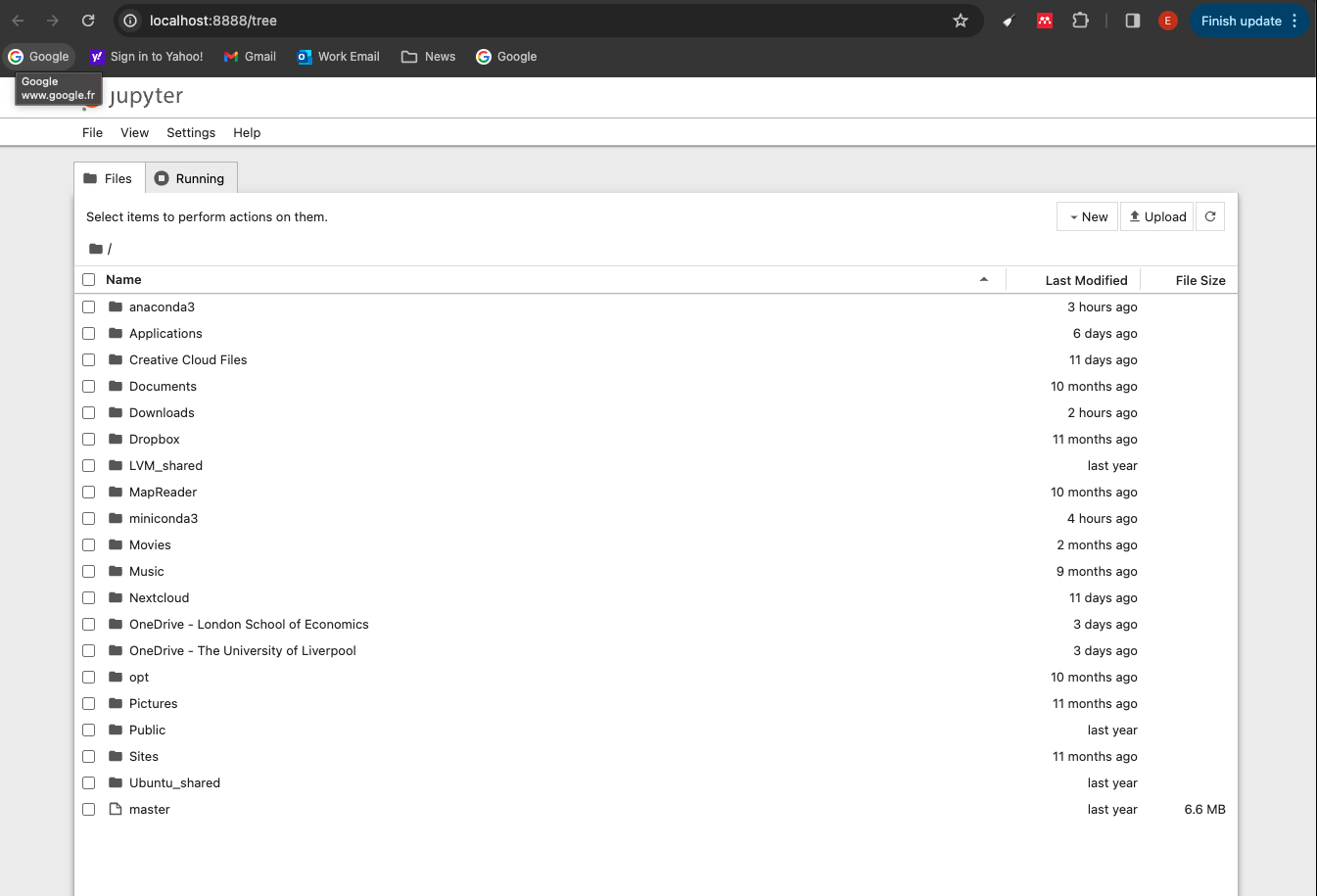
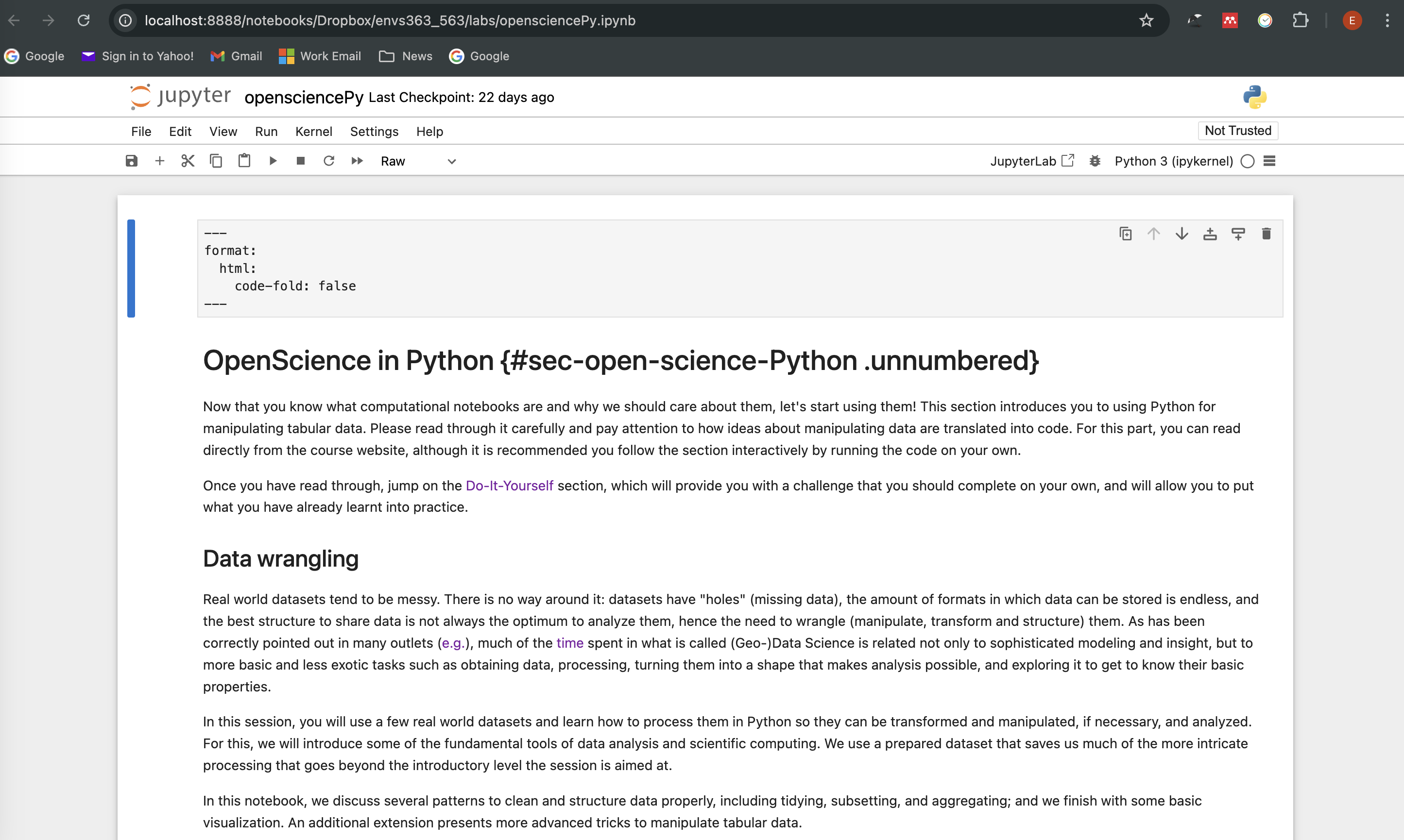
- Navigate to your folder. You can now work on your copy of the notebook.
Py Basics
Please refer to the tutorials from learnpython.org for an introduction to coding in Python. We particularly recommend the tutorials listed under the “Learn the Basics” section.
Resources
Some help along the way with: